Artificial Intelligence has rapidly evolved, with AI agents playing a crucial role in decision-making, automation, and problem-solving across industries. Understanding different types of AI agents is essential for businesses, developers, and AI enthusiasts looking to harness their full potential.
Table Of Contents
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous systems that perceive their environment, process data, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents operate in various domains, from chatbots and automation tools to advanced decision-making systems.
Characteristics of AI Agents
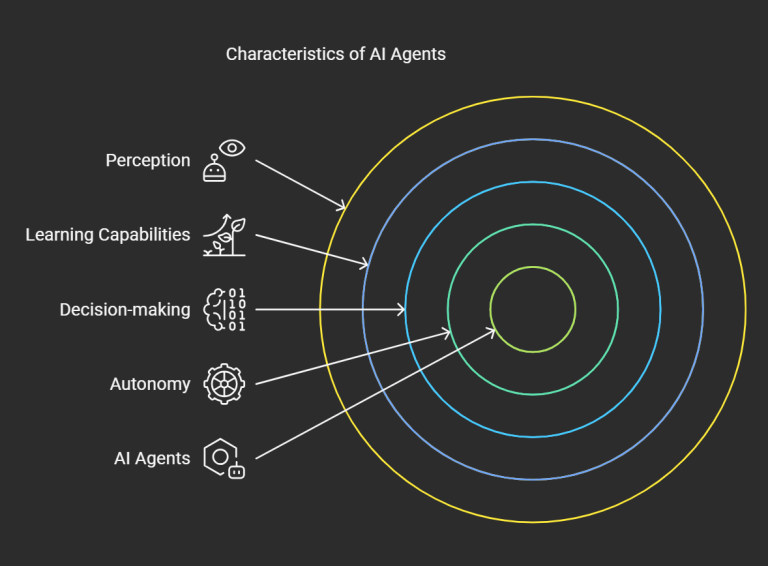
- Perception: Ability to sense the environment via sensors or data feeds.
- Decision-making: Uses algorithms to analyze data and determine the best course of action.
- Autonomy: Operates without continuous human intervention.
- Learning Capabilities: Improves over time using machine learning (ML) and reinforcement learning (RL).
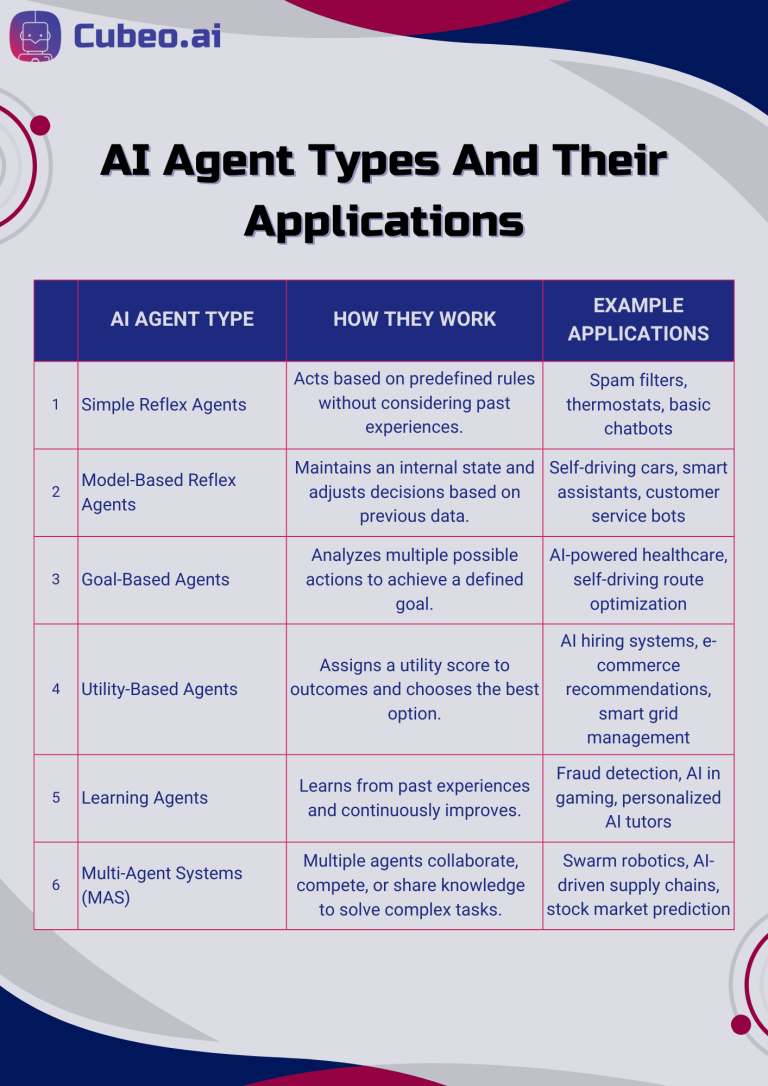
Now, let’s explore the six main types of AI agents and their applications.
Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents act solely based on current conditions, ignoring past experiences. They rely on predefined if-then rules to take action.
How They Work:
- Perceive an input
- Match it with a predefined condition
- Execute the corresponding action
Example Applications:
- Spam filters that block emails based on specific keywords
- Thermostats adjusting temperature based on sensor readings
- Rule-based chatbots offering predefined responses
📖 Read more about AI rule-based systems: IBM AI Think
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents maintain an internal state, allowing them to make more informed decisions based on past interactions.
How They Work:
- Store historical data about the environment
- Use that data to predict future conditions
- Adjust responses dynamically
Example Applications:
- Autonomous robots using past navigation data to avoid obstacles
- Smart home assistants learning user preferences
- Customer service bots remembering previous interactions
📖 Further reading on AI automation: GeeksforGeeks AI Agents
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents analyze multiple potential actions before selecting the best one that leads to a specific goal.
How They Work:
- Define an objective
- Evaluate different paths to achieve the objective
- Choose the most efficient action
Example Applications:
- Self-driving cars calculating optimal routes
- AI-powered healthcare diagnostics suggesting treatment plans
- AI trading bots predicting market trends for investment decisions
📖 More on goal-driven AI: Digital Ocean AI Agents
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents quantify success by assigning a score to different outcomes, optimizing decisions based on maximum utility.
How They Work:
- Weigh possible actions based on rewards
- Select the action with the highest utility score
Example Applications:
- AI-powered hiring systems selecting top candidates
- E-commerce recommendation engines optimizing product suggestions
- Smart grid energy management balancing power distribution
📖 Read about AI optimization models: Unstop Blog
Learning Agents
Learning agents continuously improve their performance using machine learning algorithms. They adapt through experience and self-modification.
How They Work:
- Observe results from actions
- Adjust future behavior based on past experiences
Example Applications:
- AI fraud detection systems that evolve based on new fraud patterns
- AI in gaming that learns from player behavior
- Personalized AI tutors adapting to individual learning styles
📖 Explore AI and ML integration: JavatPoint AI
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Multi-agent systems involve multiple AI agents working together to achieve complex objectives. These systems communicate, collaborate, and compete.
How They Work:
- Agents interact and share knowledge
- Some agents cooperate, while others compete
- Collectively achieve goals that a single agent cannot
Example Applications:
- Swarm robotics in search-and-rescue missions
- AI-driven supply chain optimization
- Stock market prediction systems using multiple data sources
📖 Learn about multi-agent AI: Alltius AI Glossary
How Cubeo AI is innovating AI Agent Technology
At Cubeo AI, we’re revolutionizing the way businesses implement AI agents by offering no-code AI automation. With Cubeo AI, you can:
- Create custom AI agents for research, lead enrichment, and competitor analysis
- Integrate AI with CRMs like HubSpot & Salesforce
- Automate repetitive tasks using AI-driven workflows
- Enhance business efficiency without coding expertise
🚀 Ready to leverage AI automation? Start with Cubeo AI today!
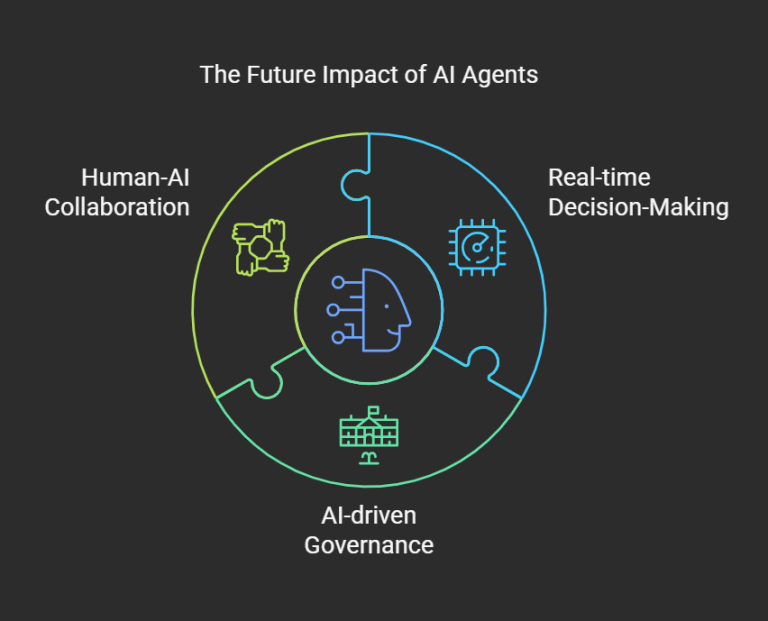
The Future of AI Agents
With advancements in AI, autonomous AI agents will soon be capable of:
- Real-time decision-making with higher accuracy
- AI-driven governance & automation in industries
- Human-AI collaboration for complex problem-solving
As we move deeper into 2025 and beyond, AI agents will continue reshaping industries, making businesses more efficient, data-driven, and automated.
Final Thoughts
AI agents are transforming the way machines interact, learn, and optimize operations. Whether in automation, finance, healthcare, or e-commerce, AI agents are reshaping the world around us.